Common HTTP Status Codes
When a client (browser, API client) makes a request to a server, the server responds with a status code.
These codes are standardized by the HTTP specification and indicate the result of the request.
1. Structure of HTTP Codes
- 3-digit numbers grouped by category:
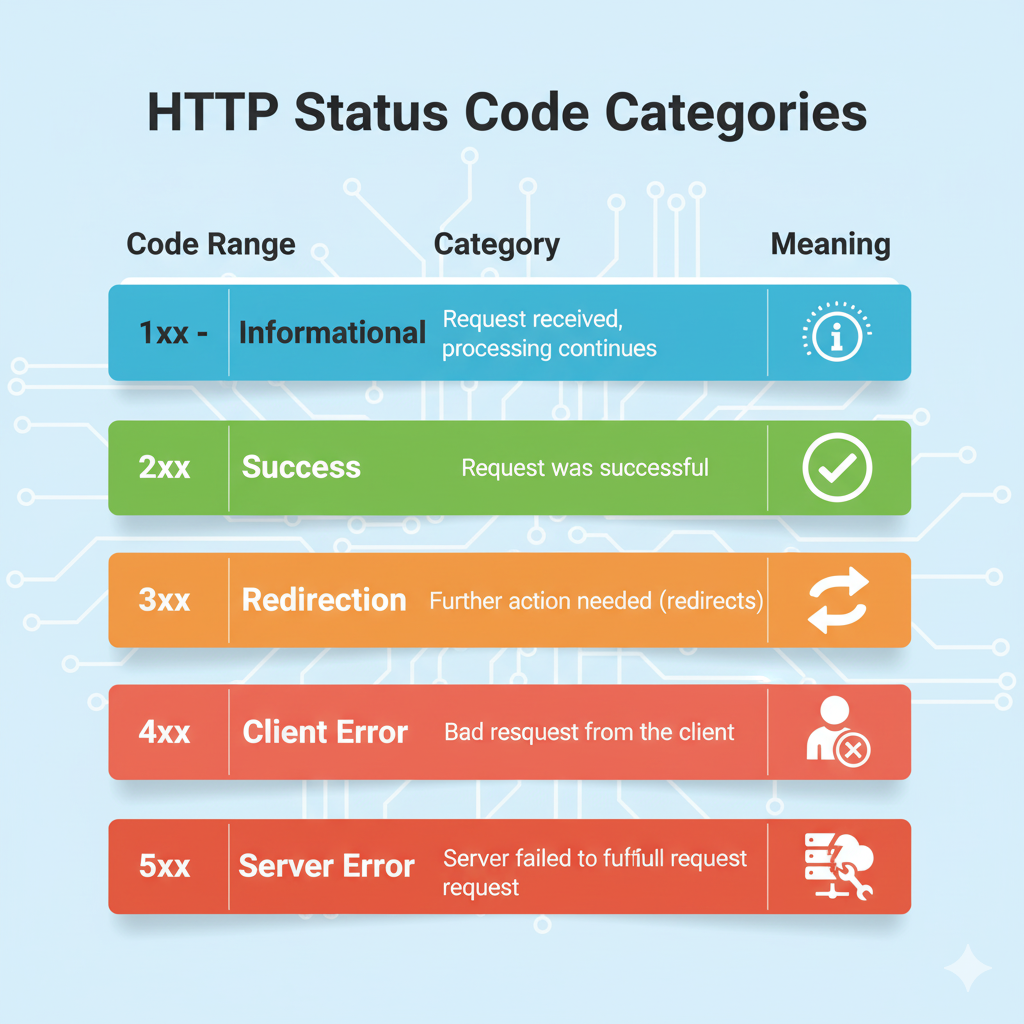
| Code Range | Category | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| 1xx | Informational | Request received, processing continues |
| 2xx | Success | Request was successful |
| 3xx | Redirection | Further action needed (redirects) |
| 4xx | Client Error | Bad request from the client |
| 5xx | Server Error | Server failed to fulfill request |
2. Informational Codes (1xx)
- 100 Continue → Client should continue sending request body.
- 101 Switching Protocols → Server agrees to upgrade (e.g., WebSocket).
- 103 Early Hints → Preload resources while response is being prepared.
3. Success Codes (2xx)
- 200 OK → Request succeeded.
- 201 Created → New resource created (e.g.,
POST /users). - 202 Accepted → Request accepted, processing happens asynchronously.
- 204 No Content → Success, but no response body.
- 206 Partial Content → Partial response, used for range requests (e.g., video streaming).
4. Redirection Codes (3xx)
- 301 Moved Permanently → Resource moved, update bookmarks.
- 302 Found → Temporary redirect (not cache-safe).
- 303 See Other → Redirect with
GETafterPOST. - 304 Not Modified → Use cached version, no need to re-download.
- 307 Temporary Redirect → Like 302, but preserves method.
- 308 Permanent Redirect → Like 301, but preserves method.
5. Client Error Codes (4xx)
- 400 Bad Request → Invalid request syntax.
- 401 Unauthorized → Authentication required (or invalid).
- 403 Forbidden → Authenticated, but not allowed.
- 404 Not Found → Resource doesn’t exist.
- 405 Method Not Allowed → HTTP method not supported for resource.
- 410 Gone → Resource permanently removed.
- 415 Unsupported Media Type → Server doesn’t support request payload type.
- 422 Unprocessable Entity → Semantic error (common in REST APIs).
- 429 Too Many Requests → Rate limiting applied.
6. Server Error Codes (5xx)
- 500 Internal Server Error → Generic server failure.
- 501 Not Implemented → Method not supported by server.
- 502 Bad Gateway → Upstream server returned invalid response.
- 503 Service Unavailable → Server overloaded or down for maintenance.
- 504 Gateway Timeout → Upstream server didn’t respond in time.
- 505 HTTP Version Not Supported → Server doesn’t support requested protocol.
7. Interview Tips
401 vs 403 vs 404 →
- 401 = not authenticated.
- 403 = authenticated but not authorized.
- 404 = resource doesn’t exist.
304 → Mention in system design interviews (saves bandwidth via caching).
206 Partial Content → Critical for media streaming and resumable downloads.
429 → Common for API rate limiting.
5xx vs 4xx → 5xx = server/infrastructure issue, 4xx = client issue.