OSI vs TCP/IP Model
Networking is the backbone of modern distributed systems.
To understand how data travels across the internet, we need a clear picture of the OSI model and the TCP/IP model.
Mnemonics to remember OSI model
Please Do Not Throw Sausage Pizza Away
(Physical, Data link, Network, Transport, Session, Presentation, Application)
1. OSI Model (Open Systems Interconnection)
The OSI model is a conceptual framework created by ISO to standardize network communication.
It divides communication into 7 layers, each with a specific role.
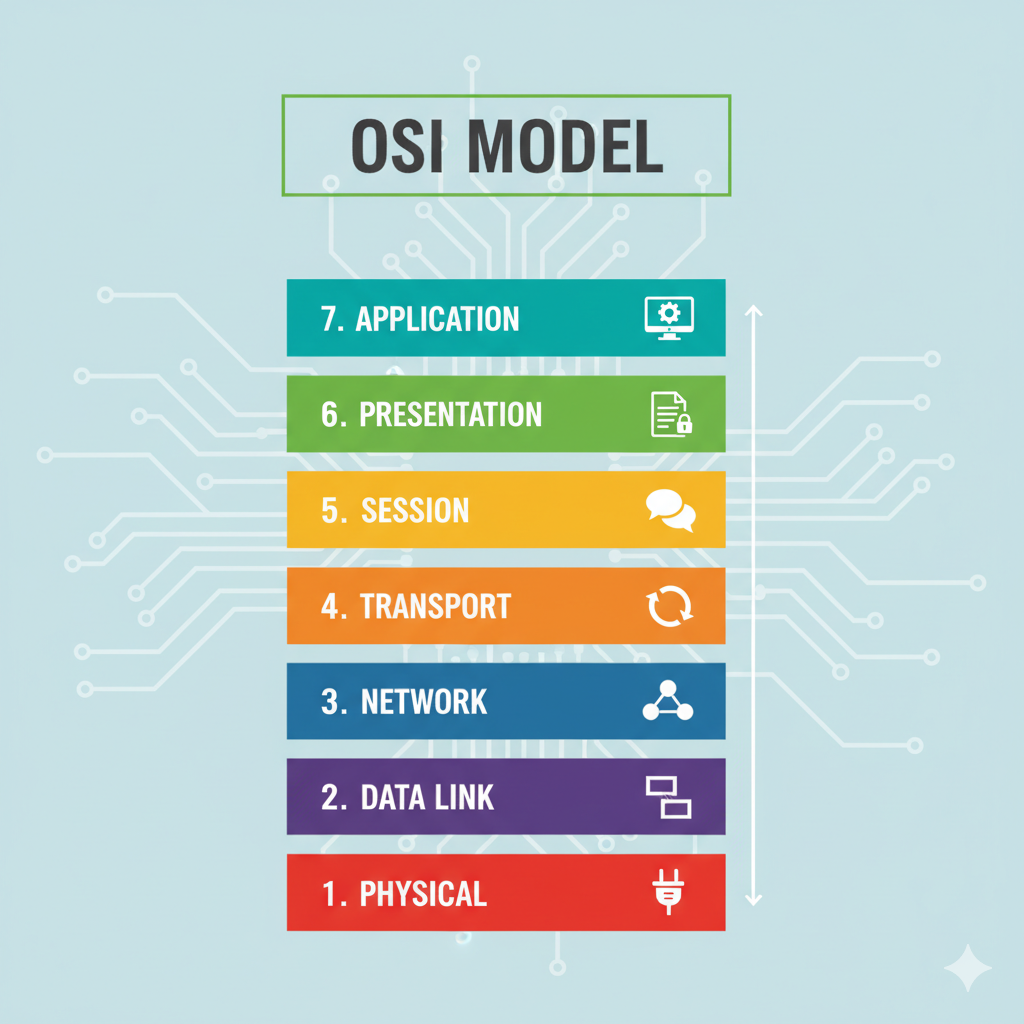
Layers of OSI Model
Physical Layer
- Deals with raw data transmission (bits).
- Cables, switches, radio frequencies.
Data Link Layer
- Provides node-to-node delivery.
- Error detection & correction.
- Examples: Ethernet, Wi-Fi (802.11).
Network Layer
- Responsible for addressing & routing.
- Example: IP (IPv4, IPv6).
Transport Layer
- End-to-end communication, reliability.
- TCP (reliable), UDP (fast, unreliable).
Session Layer
- Manages sessions (open/close connections).
- Example: NetBIOS, RPC.
Presentation Layer
- Data translation, encryption, compression.
- Example: SSL/TLS, JPEG, ASCII.
Application Layer
- User-facing services.
- Example: HTTP, FTP, SMTP, DNS.
2. TCP/IP Model (Internet Protocol Suite)
The TCP/IP model is the practical framework used in the real internet.
It has 4 layers (sometimes 5, depending on variant).
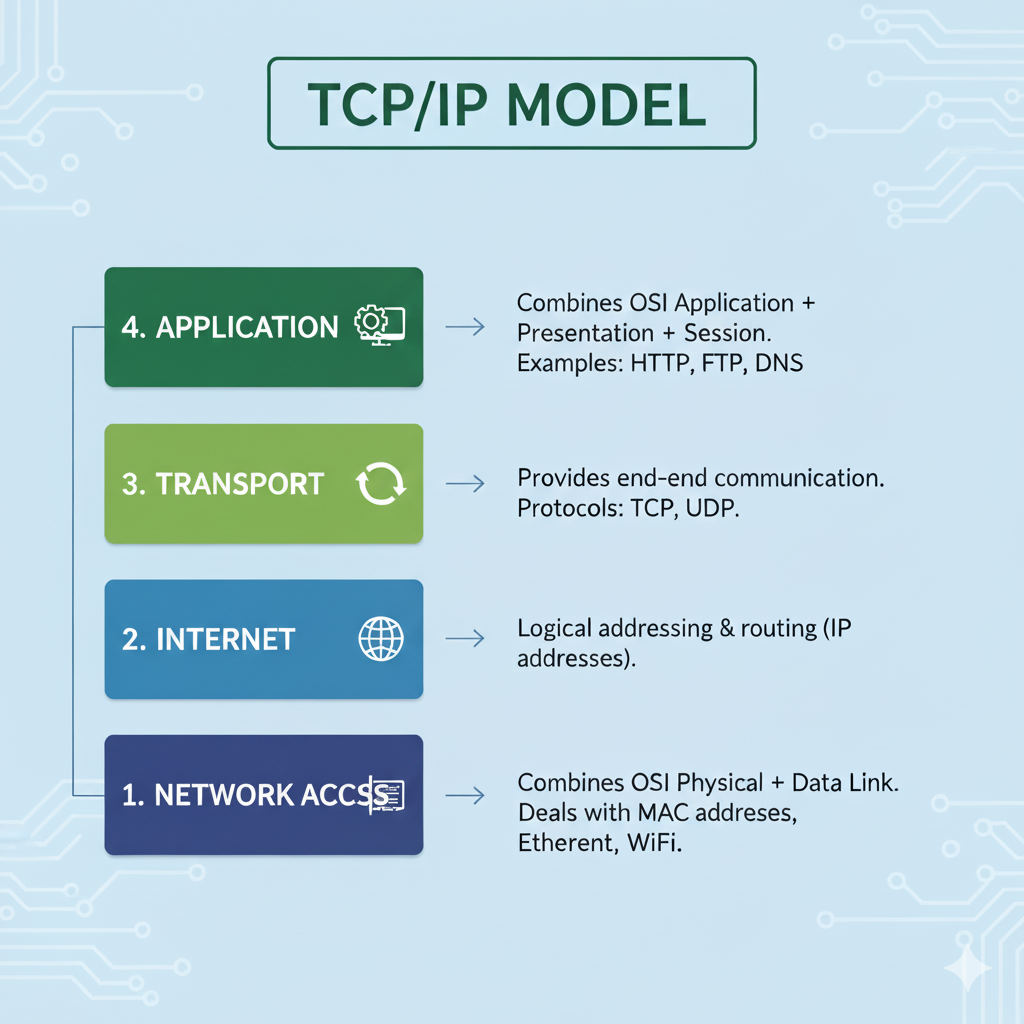
Layers of TCP/IP Model
Network Access Layer
- Combines OSI Physical + Data Link.
- Deals with MAC addresses, Ethernet, Wi-Fi.
Internet Layer
- Equivalent to OSI Network Layer.
- Provides addressing & routing (IP).
Transport Layer
- Same as OSI Transport Layer.
- TCP, UDP.
Application Layer
- Combines OSI Application + Presentation + Session.
- Example: HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, DNS, SMTP.
3. OSI vs TCP/IP: Side-by-Side
| OSI Model (7 Layers) | TCP/IP Model (4 Layers) | Example Protocols |
|---|---|---|
| 7. Application | Application | HTTP, FTP, SMTP, DNS |
| 6. Presentation | Application | SSL/TLS, JPEG, ASCII |
| 5. Session | Application | RPC, NetBIOS |
| 4. Transport | Transport | TCP, UDP |
| 3. Network | Internet | IP, ICMP, ARP |
| 2. Data Link | Network Access | Ethernet, Wi-Fi |
| 1. Physical | Network Access | Cables, radio signals |
4. Key Differences
- OSI is a theoretical model, rarely used directly in implementations.
- TCP/IP is a practical model, used in the real internet.
- OSI separates Presentation and Session layers, TCP/IP merges them into Application.
- TCP/IP is simpler, OSI is more descriptive.